Numbering
genomic reference sequences
- genomic reference sequence nucleotide numbering is g.1, g.2, g.3, …, etc. from the first to the last nucleotide of the reference sequence. Nucleotide numbers based on a genomic reference sequence do not include “+”, “-“, “*” or other prefixes.
- circular reference sequence nucleotide numbering is o.1, o.2, o.3, …, etc. from the first to the last nucleotide of the reference sequence. Nucleotide numbers based on a circualr reference sequence do not include “+”, “-“, “*” or other prefixes.
- mitochondrial DNA reference sequence
a mitochnodrial reference sequence is a special circular genomic reference sequence. Nucleotide numbering is m.1, m.2, m.3, …., etc. from the first to the last nucleotide of the reference sequence. Nucleotide numbers based on a mitochondrial reference sequence do not include “+”, “-“, “*” or other prefixes.
- the preferred human mtDNA reference sequence is the Homo sapiens mitochondrion, complete genome (GenBank NC_012920.1).
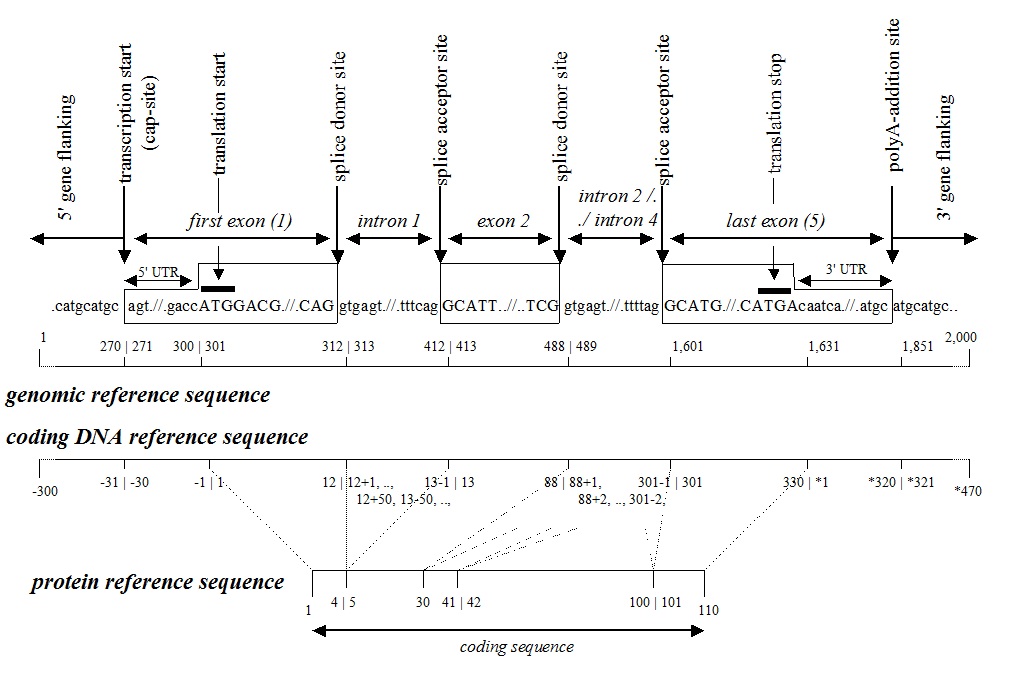
coding DNA reference sequences
nucleotide numbering is based on the annotated protein isoform, the major translation product.
-
- protein coding region
- numbering starts with “c.1” at the A of the ATG translation initiation (start) codon and ends with the last nucleotide of the translation termination (stop) codon, i.e. TAA, TAG, or TGA.
-
- exception 3’ rule
- the 3’ rule is not applied when there is a deletion/duplication around exon/exon junctions with identical nucleotides flanking the junction, where shifting the variant 3’ would place it in the next exon. Projecting the variant from c. back to g. positions (genomic) would then lead to an incorrect genomic position (in the wrong exon)
- When ..GAT gta..//..cag TCA.. changes to ..GA_ gta..//..cag TCA.., based on a coding DNA reference sequence the variant is described as LRG_199t1:c.3921del (NC_000023.10:g.32459297del) and not as c.3922del (which would translate to g.32456507del)
- NOTE: this exception does not apply to a deletion/duplication around exon/intron and intron/exon junctions with identical nucleotides flanking the junction (see also Deletions)
- untranslated region (UTR)
- nucleotides upstream (5’) of the ATG-translation initiation codon (start) are marked with a “-” (minus) and numbered c.-1, c.-2, c.-3, etc. (i.e. going further upstream)
- nucleotides downstream (3’) of the translation termination codon (stop) are marked with a “*” (asterisk) and numbered c.*1, c.*2, c.*3, etc. (i.e. going further downstream)
- there is no nucleotide c.0.
- introns
- nucleotides at the 5’ end of an intron are numbered relative to the last nucleotide of the directly upstream exon, followed by a “+” (plus) and their position in to the intron, like c.87+1, c.87+2, c.87+3, …
- nucleotides at the 3’ end of an intron are numbered relative to the first nucleotide of the directly downstream exon, followed by a “-” (minus) and their position out of the intron, like …, c.88-3, c.88-2, c.88-1.
- in the middle of the intron nucleotide numbering changes from “+” (plus) to “-” (minus): e.g. …, c.87+676, c.87+677, c.87+678, c.88-678, c.88-677, c.88-676, …
- in introns with an uneven number of nucleotides the central nucleotide is numbered relative to the upstream exon followed by a “+” (plus): e.g. …, c.87+676, c.87+677, c.87+678, c.87+679, c.88-678, c.88-677, c.88-676, …
- introns in the 5’UTR are numbered as normal introns, starting with “c.-” nucleotide numbers (c.-85+1, c.-85+2, c.-85+3, …, c.-84-3, c.-84-2, c.-84-1)
- introns in the 3’UTR are numbered as normal introns, starting with “c.*” nucleotide numbers (c.*37+1, c.*37+2, c.*37+3, …, c.*38-3, c.*38-2, c.*38-1)
- NOTE: a coding DNA reference sequence does not contain intron or 5’ and 3’ gene flanking sequences and can therefore not be used as a reference to describe variants in these regions see Reference Sequences. Correct descriptions refer to a genomic reference sequence like LRG_199t1:c.357+1G>A, NC_000023.10(NM_004006.2):c.357+1G>A or NG_012232.1(NM_004006.2):c.357+1G>A.
-
- transcript flanking
- it is not allowed to describe variants in nucleotides beyond the boundaries of the reference sequence using the reference sequence
- suggestions made to extend the recommendations for nucleotide numbering of coding DNA reference sequences to specifically mark non-transcribed nucleotides have been made but were rejected (see Open Issues).
Initial recommendations (Antonarakis (1998) and Den Dunnen & Antonarakis (2000)) suggested two alternative descriptions for intronic variants; c.88+2T>G / c.89-1G>T and c.IVS2+2T>G / c.IVS2-1G>T. The format c.IVS2+2T>G / c.IVS2-1G>T has been retracted and should not be used.
non-coding DNA reference sequences
- nucleotide numbering is n.1, n.2, n.3, …, etc. from the first to the last nucleotide of the reference sequence
- nucleotides in introns are numbered as for coding DNA reference sequences (see above), although preceeded by n. (not c.)
- it is not allowed to describe variants in nucleotides which are not covered by the transcript using a non-coding DNA reference sequence
RNA reference sequences
nucleotide numbering for a RNA reference sequence follows that of the associated coding or non-coding DNA reference sequence; nucleotide r.123 relates to c.123 or n.123.
- in a non-coding RNA reference sequences nucleotide numbering is r.1, r.2, r.3, …, etc. from the first to the last nucleotide of the reference sequence.
- in a coding RNA reference sequences nucleotide numbering is based on the annotated protein isoform, the major translation product, following that of a coding DNA reference sequence see coding DNA reference sequence.
- coding/non-coding RNA reference sequences do not contain intron sequences and can therefore not be used to describe variants affecting these sequences see Reference Sequences. Correct descriptions therefore need to give a genomic reference sequence like LRG_199t1:r.186_187ins186+1_186+4, NC_000023.10(NM_004006.2):r.186_187ins186+1_186+4 or NG_012232.1(NM_004006.2):r.186_187ins186+1_186+4.
protein reference sequences
amino acid numbering is p.1, p.2, p.3, …, etc. from the first to the last amino acid of the reference sequence
- amino acid numbers based on a protein reference sequence may include a “-“ or “*” prefix (see Protein Extensions).
Q&A
-
- Why do people prefer to report variants based on a coding DNA reference sequence?
- This topic is discussed on the Reference sequences page. The two main reasons are that descriptions are 1) shorter then those based on a chromosomal genomic reference sequence (e.g. NC_000006.11:g.117198495_117198496del compared to LRG_199t1:c.57_58del) and 2) give some idea where the variant is located regarding the encoded gene product (RNA and protein).
-
- c.78T>C is a variant in a protein coding sequence
- since nucleotide “c.78” has no signs attached and is not followed by a “+” or “-“ and a second number it is located in the protein coding part of the gene.
- NOTE: this rules does not hold for alternative transcripts where exons might reside 5’ of the translation initiation side, in an intron or 3’ of the 3’-terminal exon.
- NOTE: dividing the nucleotide number by 3 gives the number of the amino acid residue affected, in the example amino acid 26 (78:3 = 26).
-
- c.-78G>A is a variant upstream (5’) of the translation initiation site
- since nucleotide “c.-78” has a “-” prefix it is located 5’ of the ATG translation initiation codon.
- NOTE: the length of the 5’UTR determines whether this nucleotide is still part of the transcript or upstream of the transcription initiation site (cap site).
-
- c.*78T>A is a variant downstream (3’) of the translation termination site
- since nucleotide “c.*78” has a “*” prefix it is located 3’ of the translation termination codon
- NOTE: the length of the 3’UTR determines whether this nucleotide is still part of the transcript or downstream of the polyA-addition site.
-
- c.78+45T>G is a variant in an intron (5’ half)
- since nucleotide “c.78” is followed by “+” and a second number (“45”) the nucleotide is in an intron, 3’ of the splice donor site and in the 5’ half of the intron
-
- c.79-45G>T is a variant in an intron (3’ half)
- since nucleotide “c.79” is followed by “-” and a second number (“45”) the nucleotide is in an intron, 5’ of the splice acceptor site and in the 3’ half of the intron
-
- c.-106+2T>A is a variant in an intron in the 5’UTR (upstream of the translation initiation site)
- since nucleotide “c.-106” has a “-” prefix it is located 5’ of the ATG translation initiation codon and since it is followed by “+” and a second number (“2”) the nucleotide is in the 5’ half of an intron
-
- c.*639-1G>A is a variant in an intron in the 3’UTR (downstream of the translation termination site)
- since nucleotide “c.*639” has a “*” prefix it is located 3’ of the translation termination codon and since it is followed by “-” and a second number (“1”) the nucleotide is in the 3’ half of the intron
-
- When I retrieve a coding DNA sequence from GenBank (NM_ file) nucleotide numbering does not start with 1 at the A of the ATG translation initiation codon.
- Correct, but it is not difficult to obtain such a file. Go to the NM_ sequence of interest using the Nucleotide database, e.g. NM_004006.2. The page retrieved is annotated extensively. Clicking the “CDS” annotation (CoDing Sequence) opens a window where the nucleotide numbering will start with 1 at the A of the ATG translation initiation (start) codon.
- To assist those studying or reporting sequence variants, gene variant databases (LSDBs, see the HGVS list of LSDBs) usually provide a coding DNA reference sequence with the nucleotide numbering displayed (see e.g. the DMD example)
-
- Why was the recommendation to describe intronic variants using the c.IVS notation (c.IVS2+2T>G / c.IVS2-1G>T) been retracted?
- For descriptions like c.IVS2+2T>G / c.IVS2-1G>T it is difficult to deduce where the position of the intron relative to the coding DNA reference sequence is. First, many authors fail to mention the genomic and coding DNA reference sequences that were used as a basis of exon/intron numbering. Second, since many genes encode several transcripts exon numbers will be different for each transcript. Descriptions using the format c.IVS2+2T>G thus fail the basic criterion to be unequivocal and should not be used. Descriptions using the format c.88+2T>G do not suffer from these problems.
- NOTE: when intronic variants are described in relation to a coding DNA reference sequence authors should not forget to give the genomic reference sequence containing the intron sequences.
-
- Why are intronic nucleotides not simply numbered from +1 to the end, i.e. with a + (plus) only, without changing in the middle to a - (minus) numbering?
- It is more informative. When a change in an intron is described as c.88+4356A>G, in stead of c.89-2A>G, it will not be clear that the change is close to the splice acceptor site, and might thus affect splicing. In addition, the swap makes variant descriptions for all nucleotides towards the 3’end of an intron shorter.
-
- When the ATG translation initiation codon is in exon 2, and we find a variant in exon 1, should we include intron 1 (upstream of c.-14) in nucleotide numbering? (Isabelle Touitou, Montpellier, France)
- Nucleotides in introns 5’ of the ATG translation initiation codon (i.e. in the 5’UTR) are numbered as introns in the protein coding sequence (see coding DNA numbering). In your example, based on a coding DNA reference sequence, the intron is present between nucleotides c.-15 and c.-14. The nucleotides for this intron are numbered as c.-15+1, c.-15+2, c.-15+3, …., c.-14-3, c.-14-2, c.-14-1. Consequently, regarding the question, when a coding DNA reference sequence is used, the intronic nucleotides are not counted.
-
- Recently two previously unidentified exons of the TCOF1 gene were identified, and named 6A and 16A. Exon 6A is present in most of the transcripts, exon 16A is included only in a few transcripts. In updating the nomenclature of reported variants in TCOF1, should I use a sequence that corresponds to the major transcript (with exon 6A, but without 16A) or to the longest (“most complete”) transcript variant? (Alessandra Splendore, Rio de Janeiro, Brasil)
- This is the main problem of describing variants based on a coding DNA reference sequence, relative to a genomic reference sequence descriptions would be stable. When variants are reported in relation to a transcript, the preferred reference sequence is the reference suggested by the MANE project (see Ensembl or NCBI).
-
- How to describe variants in ZRS, a regulatory sequence for the SHH gene that lies 1 Mb upstream of SHH in intron 5 of the LMBR1 gene? (Tracy Lester, Oxford, UK)
- NOTE: Variants in ZRS are associated with various limb abnormalities and to-date have been numbered according to a sequence which does not follow HGVS guidelines. Should we create a genomic reference sequence for SHH that includes 1 Mb of upstream sequence to encompass the ZRS region or should we number it according to the LMBR1 reference sequence?
- A difficult case. We see 2 options;
- simply describe the variants using a genomic reference sequence.
- describe the variant in the LMBR1 gene variant database, which uses NM_022458.3 as a reference transcript. To link the variant to SHH you can add that no variants were found in the SHH gene (description c.=), classify it as “Affects function” and mention the effect of the variant on transcription/translation. This ensures the variant will be listed in the SHH database overview.
-
- The recommendation for nucleotide numbering in a gene based on a genomic reference sequence works only if the reference sequence in the database is published as a single file. For my organism there is not yet a reliable genome assembly. For my gene of interest the genomic sequence is stored in multiple files, each containing one exon and partial flanking intron sequences. What should I do?
- If no database file is available that contains the complete genomic sequence, such a file should be constructed and submitted to the database. For unsequenced sections in the introns N’s can be used to fill gaps (the number of N’s included can be used to get the intron to the estimated size). The accession.version number of the submitted file can than be used as a genomic reference sequence.
Figure
Examples
The basic recommendation is that the reference sequence used represents the major and largest transcript of the gene. The MANE Select transcript available from the MANE project (see Ensembl or NCBI) is preferred if it is a suitable reference for describing the variant. Variants present in alternative transcripts, not covered by the selected reference transcript, can be described based on annotated alternative transcript variants (e.g. NM_001099404.2, LRG_199t3) or protein isoforms (e.g. NP_001092874.1, LRG_199p3), preferring MANE Plus Clinical transcripts if specified by the MANE project. Contact the MANE project (MANE-help@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov or mane-help@ebi.ac.uk) if any pathogenic variants cannot be adequately described using available MANE transcripts.
- alternative promoter
- 5’ of the major transcript, e.g. Dp427c brain-specific transcript 5’ of the DMD gene
- inside gene, e.g. Dp260 retina-specific transcript in intron 29 of the DMD gene
-
- introns in 5’ untranslated region (UTR)
- e.g. three introns in the 5’UTR of the FKRP gene, for numbering see coding DNA numbering
- alternatively spliced exon
- alternative 3’ terminal exon
- inside gene
- directly 3’ of an exon; e.g. exon/intron 10 in the LMNA gene
- completely in an intron; e.g. in intron 47 of the TTN gene
- after gene (in gene downstream sequence)
- inside gene
- introns in 3’ untranslated region (UTR) * when an intron immediately follows the last nucleotide of the translation termination (stop) codon (e.g. position c.876), nucleotides in the intron are numbered like c.876+1, c.876+2, c.876+3, …, c.*1-3, c.*1-2, c.*1-1.